Voices from the Sylff Community
Jul 28, 2017
Jewish Religious Life in the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic
Karina Barkane, a 2014 Sylff fellow from the University of Latvia, visited the YIVO Institute for Jewish Research in the United States to reveal unexplored aspects of Jewish religious life in the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic (1944–90) using an SRA award. In this article she describes the challenge of preserving Jewish religious and cultural identity under the Soviet regime in the historical context of secularization and assimilation.
* * *
Introduction
My interest in Jewish history was sparked by my grandfather, who told me many fascinating stories about the Jewish people and their religion. I was captivated by its temporal and spatial breadth. Since its inception over several thousand years ago, Jewish religion has been influenced by other cultures. With a remarkable ability to adapt to changing circumstances, the Jewish people and religion have overcome persecution and flourished over the centuries, integrating cultural assumptions of the neighboring communities into their own social and religious systems and preserving a distinct identity.
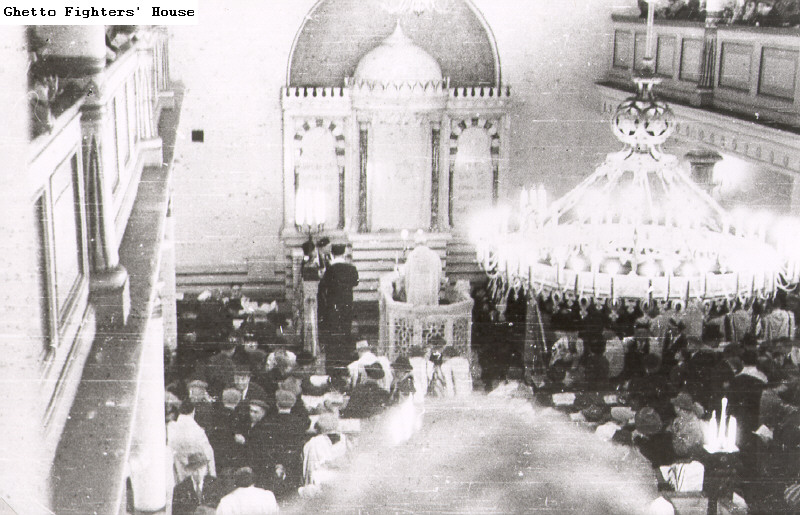
A prayer service in the synagogue in Riga during Soviet times. Photo: The Ghetto Fighters' House Archives.
Growing assimilation and integration with surrounding cultures have given rise to the fundamental question: What does it mean to be a Jew? Is it a religious identity, ethnic identity, or a combination of the two? Moreover, as Judaism encompasses a way of life, wherein the religious element cannot be completely separated from the secular, the issue is made that much more complex and remains open to the present day.
Jews in Latvia
Diversity has also characterized the history of the Jewish community in Latvia. Jews who immigrated to Latvia came from different regions. The first Jews came from Prussia and settled in Courland (western Latvia) at the end of the sixteenth century. They were well-educated and influenced by German culture. Meanwhile, Jews in Latgale (eastern Latvia) first appeared in the mid-seventeenth century and were closer to the traditional Lithuanian and Russian Jewish communities. They were less educated than the Courland Jews but more strictly observed religion.
By the end of the nineteenth century Jews comprised a substantial part of Latvia’s population. In some cities they accounted for around half of the entire population: 69.6% of the population in Jaunjelgava, 59.4% in Bauska, 54.5% in Ludza, 54.0% in Rēzekne, and 49.0% in Valdemārpils.[1] The majority of the synagogues in Latvia, which had a number of outstanding rabbis, were built during this period.
After the establishment of the independent Republic of Latvia (1918–40), Jews in Latvia were granted all the rights of citizenship and could freely express and develop their religion and identity. There numbered more than 200 Jewish religious communities formed by socially diverse people, from prominent manufacturers to ordinary craftsmen.
Fundamental changes occurred over the years, however. These changes were connected not only with the Holocaust but also with the shifting power structure. In 1944 Latvia was forcibly incorporated into the Soviet Union. The Communist Party secured its monopoly on all spheres of public life and sought to transform society. This affected the cultural and social roles that Jews could play in Latvia and had a tremendous impact on Jewish religious life.
My Doctoral Dissertation Research
My doctoral dissertation is devoted to the challenging question of preserving Jewish religious identity under the Soviet regime in the context of secularization and assimilation. As the majority of studies on Jews in Latvia look at the period until the middle of the twentieth century, with the Holocaust as an end point, almost no research has been carried out on the issue to this day and the history of Jews and Judaism during the Soviet era remains a blank page in the history of Latvia. Scientific publications on this topic cover only particular aspects and periods—primarily the issue of anti-Semitism and the Jews’ struggle for the right to emigrate from the USSR—and are scattered across different journals and books that are focused on broader topics.
The main aim of the dissertation is to conduct an in-depth study on Jewish religious life in the Latvian SSR (1944–90) after the Holocaust. Specifically, it seeks to reveal the ideology of and legislation by Soviet power, as well as the local authority’s attitude toward Jews and Judaism; analyze the activities of Jewish religious communities, focusing on their spiritual, social, and financial life; and characterize individual and family traditions among Jews during this period.
The preliminary results are summarized in the following sections.
The Soviet Attitude toward Judaism
The Soviet regime’s attitude toward Judaism was determined to a certain extent by its religious policy, which was based on the assumption that religion in all its forms is a harmful relic of the past that needs to disappear. The Soviet Union was the first country in the twentieth century to commit to an antireligious policy from its very inception; yet, paradoxically, the religious communities maintained their legal status, albeit under constant pressure.[2] The state used a vast apparatus of education, propaganda, and repression to implement a fundamentally antireligious doctrine. Over the years this was adjusted according to the overall social and political context, including development of the state and international relations.
Due to the strong connection between Jewish religion and nationality, which dictates that the only ethnic group practicing Judaism is the Jews, Soviet policies that affected the Jewish religion ipso facto affected the Jews and vice versa.[3]
According to the framework of Soviet policy on nationality, Jews did not conform to the “scientific” Marxist-Leninist definition of a nation and were targeted for assimilation into the dominant nation. For this reason, the existence of a “Jewish question” in the USSR was denied throughout the Soviet era, even though it perpetually stood at the center of public discussion.[4] Soviet authorities did not permit the creation of Jewish educational and cultural institutions. Jews were deprived of even the minimal cultural autonomy: there were no Jewish schools, newspapers, or theaters, for instance. During the so-called campaign against cosmopolitanism[5] of 1949–53, moreover, a number of local Jewish intellectuals were arrested and accused of bourgeois nationalism.
Under these circumstances Jewish religious communities, as the only legitimate organs of Jewish autonomy, came to primarily and, in fact, single-during this period. Even so, all of their activities were dependent on Soviet power. They were constrained by the operations of the Representative of the Council for the Affairs of Religious Cults[6] (which were carried out strictly within the politics of the CARC chairman) and by the local authority’s attitude, as well as by antireligious propaganda, which was widely disseminated throughout society.
Jewish Religious Life
By April 1949, when the process of registering religious communities was completed,[7] seven Jewish religious communities were officially registered in the Latvian SSR.[8] Of these seven communities, three were subsequently closed by authorities due to Soviet policy.
Individuals who were familiar with Jewish religious customs and agreed to undertake leadership roles were essential to keeping the spirit of the communities alive, as there was a severe shortage of rabbis owing to the Holocaust and Soviet restrictions in rabbinic ordination. Because of their substantial role, however, authorities repressed these individuals in a variety of ways: economic repression, so-called individual work, arrests, and so forth.
Maintaining a religious lifestyle was extremely difficult under the antireligious and anti-Semitic policies. The authorities tended to restrict the obtaining of ritual objects and the provision of kosher meat; attending the synagogue on Jewish holidays, when everyone was obligated to work, could call into question one’s loyalty to the regime and trigger a confrontation with authorities. Most Jews had to negotiate between integration into Soviet society and Jewish identity.
Despite the oppression, many Jews strived to preserve their ties with the synagogue and tradition—some of them directly and others disguising it. For instance, almost all religious rites, such as burials and circumcision, were practiced in secret relatively broadly among the Jewish population, even by Jews who distanced themselves from religion.
Synagogue attendance was very high on Pesach, Simchat Torah (during which a significant proportion of visitors were youth), and High Holidays, as well as on the regularly organized days to commemorate the victims of the Holocaust.[9] In 1957, for instance, around 4,000 people attended the prayers on Yom Kippur in the Riga synagogue.[10] Even Jews who were members of the Communist Party and those from the cities, where no Jewish religious communities were reestablished, came to the nearest synagogue to celebrate these holidays.
Since legitimate ways to express Jewish identity had been so narrowed, for many Jews these ties with the synagogue were an opportunity to resolve their ambivalent status—they were highly acculturated but not assimilated and remained “Jews” socially and officially.[11] Many Jews expressed their ethnic identity by means of religious practice. The religious aspect of Jewish life thus underwent a radical transformation, increasingly moving away from normative Judaism and forming a new Jewish identity based on ethnicity.
In Closing
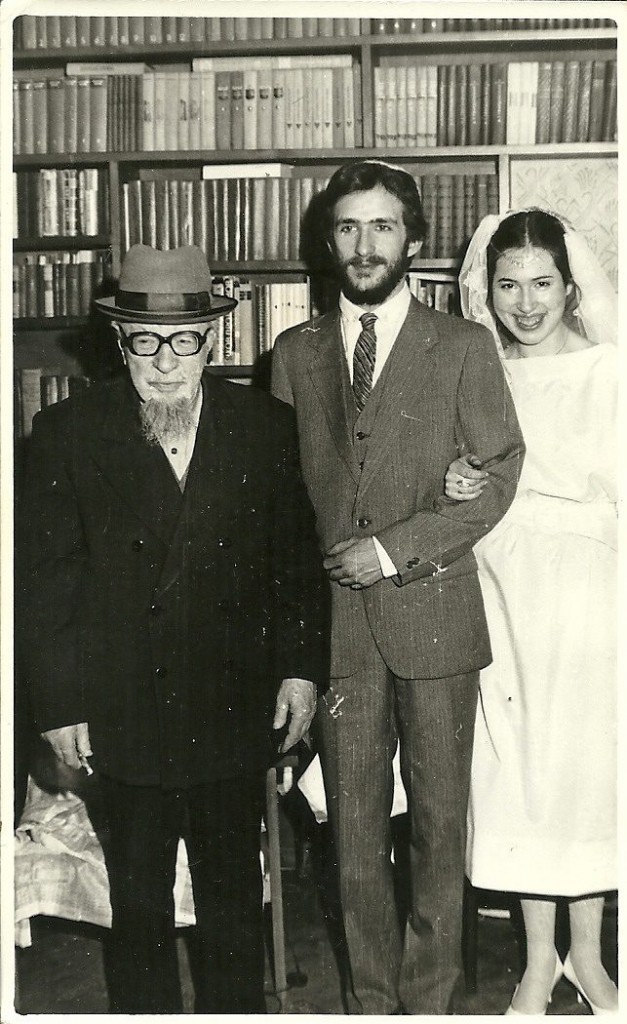

Rabbi Gershon Gurevitch , left, performing the chuppah (Jewish wedding canopy) ceremony for Shlomo Lensky, late 80-'s. Photo: Riga synagogue, Peitav-shul (http://shul.lv).
The SRA grant gave me an opportunity to conduct research at the YIVO Institute and expand the scope of historical sources for my doctoral dissertation. It allowed me to compare previously gathered sources on Soviet authorities with those from the other side of the Iron Curtain, created from different ideological viewpoints, not only revealing previously unknown or overlooked aspects but also posing many new questions for further research. I would like to greatly thank SRA for the invaluable support.
I hope that, in the long term, my research will go far beyond the local context, helping foster intercultural and interreligious understanding and encouraging sensitivity to the positions of minorities.
[1] Leo Dribins, Ebreji Latvijā [Jews in Latvia] (Rīga: Elpa, 2002), 43.
[2] Mordechai Altshuler, Religion and Jewish Identity in the Soviet Union, 1941–1964 (Waltham: Brandeis University Press, 2012), 1.
[3] Zvi Gitelman, “Jewish Nationality and Religion,” in Religion and Nationalism in Soviet and East European Politics, ed. Sabrina P. Ramet (Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 1989), 59.
[4] Naomi Blank, “Redefining the Jewish Question from Lenin to Gorbachev: Terminology or Ideology?” in Jews and Jewish Life in Russia and the Soviet Union, ed. Yaacov Ro’I, (Portland: Frank Cass, 1995), 53.
[5] Anticosmopolitan Campaign - was an anti-Semitic campaign in the Soviet Union. Cosmopolitans were Jewish intellectuals who were accused of expressing pro-Western feelings and lack of patriotism.
[6] The CARC, with representatives in the Union Republics, was established in 1944 to supervise the enforcement of Soviet legislation regarding religion and manage relations between the Soviet government and religious organizations.
[7] According to Soviet law, a religious group of believers could start its activities only after official registration with the CARC. The registration of a religious community involved many stages and prescriptions. Permission to organize a religious community was granted if the community had at least 20 persons (dvadtsatka), a prayer building, and a religious service provider (rabbi).
[8] State Archives of Latvia, coll. 1448, inv. 1, file 28, p. 3.
[9] Pesach is also known as Passover. Simchat Torah is the festival to celebrate and mark the conclusion of the annual cycle of public Torah readings. High Holidays refer to the two days of Rosh Hashanah (Jewish New Year) and Yom Kippur (Day of Atonement).
[10] State Archives of Latvia, coll. 1448, inv. 1, file 257, p. 87.
[11] Zvi Gitelman, A Century of Ambivalence: The Jews of Russia and the Soviet Union, 1881 to the Present (Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2001), 178.

Comments
Sylff staff
Karina, thank you for sharing your research results. I visited Museum of the Occupation of Latvia during my trip to Latvia University in May, 2017 and learned that people in Latvia had suffered a lot. Your article helps me understand the era in depth. Mari Suzuki