Mengtai Zhang, a 2018 Sylff fellow, utilized an SRA without Overseas Travel grant in 2021–22 to explore the fate of Hubei and other urban villages in Shenzhen, China, which are on the brink of demolition—and oblivion. Faced with COVID-19 travel restrictions, Zhang enlisted a research assistant to conduct fieldwork and interviews on his behalf. What emerges is the dilemma between economic development and such considerations as social justice and preservation of culture.
* * *
Due to China’s rapid rural urbanization in the last forty years, urban villages have become a common phenomenon, where the expansion of urban areas physically enclose rural lands operating under different land tenure. What makes urban villages unique in Shenzhen is that they are a product of segregated policies but have been restructuring the segregation from within over the last few decades. This segregation manifests in a rural-urban division and the resulting unequal allocation of institutional resources.
This division is embedded in the evolution of Shenzhen’s urban villages. With Shenzhen’s rapid economic development as a Special Economic Zone since China’s Reform and Opening Up in 1979, urban villages evolved with a level of self-organization to accommodate the large influx of migrant workers, providing them with access to superior urban resources in an affordable way, while bringing wealth to local rural collectives that own the land. This dynamics shifted from the mid-2000s, when many urban villages began to be demolished and rebuilt by mega real estate developers, often into skyscrapers and large shopping malls, under government planning. By the 2010s, more and more people in Shenzhen had started advocating for the protection of urban villages. Many wanted to preserve the urban villages for migrants and working families who were still suffering from unequal resource distribution. They also believed the urban villages bore historical significance to the rise of Shenzhen.
Collective Memory and the Case of Hubei
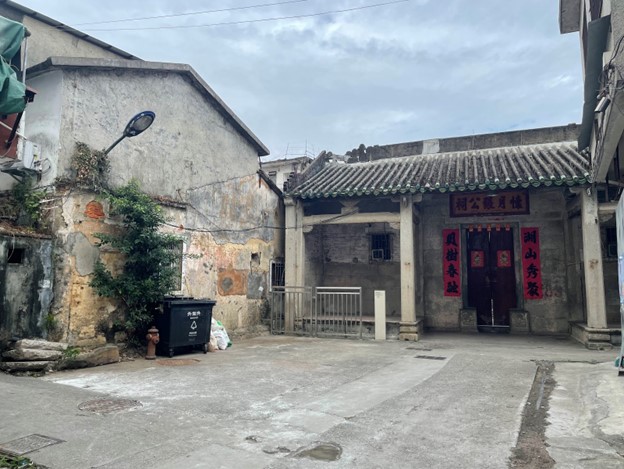
In July 2016 Hubei 120, a leaderless movement of artists, scholars, and architects, initiated a series of activities against the demolition of Hubei, an urban village in the Luohu district in central Shenzhen. As Hubei has existed for hundreds of years, participants of Hubei 120 argued that destroying Hubei would destroy Shenzhen’s shared memories and cultural assets. At the end of 2017, Hubei 120 curated a prominent art exhibition at the Bi-City Biennale of Urbanism/Architecture. I participated in the exhibition and presented two works, a soundscape composition of Hubei and a performance, both of which began during my 2016 art residency in Shenzhen. Both works used sound to create contexts about the impact of urbanization on people’s living conditions. Having captured the soundscape of Hubei when the place was facing demolition, I utilized the SRA without Overseas Travel grant to continue the research on Hubei at the end of 2021, now that demolition and reconstruction were well under way.
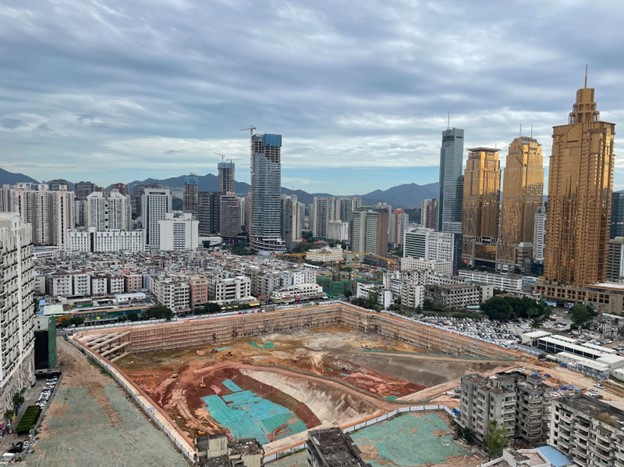

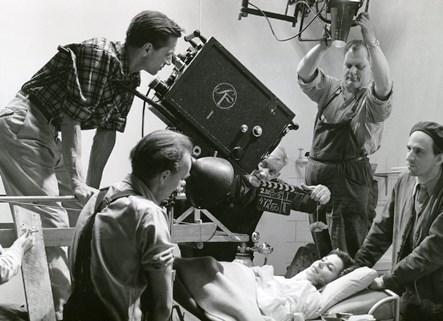
Landscape view of Hubei, demolition in progress, Shenzhen, December 2021. (Photo courtesy of Lemon Guo)
During the research period in 2021 and 2022, I explored how collective memories were impacted by other systems in the process of migration. I was interested in what urban villages meant to different groups of people in Shenzhen and what we could hear from the diverging voices on what should happen to Hubei. With the support of an SRA without Overseas Travel award from the Sylff Association, I hired research assistant Lemon Guo to conduct fieldwork and interviews in Shenzhen, since I was unable to travel to China due to COVID-19 restrictions.
Guo visited urban villages in Shenzhen, including Shangwei, Baishizhou, Shuiwei, Caiwuwei, and Hubei, and took field recordings and photographs. She mainly interviewed anthropologist Mary Ann O’Donnell, who is an expert on the urban villages in Shenzhen, and theater maker Yang Qian and filmmaker Shi Jie, both of whom were significant contributors to Hubei 120. We asked questions regarding the demolition process of Hubei, the characteristics of urban villages, and their memories of Shenzhen’s reform.
O’Donnell told us about the history of evolution of urban villages from spontaneous communities to planned communities and her memories of this process, having lived in several urban villages for most of her two-decades-plus of life in Shenzhen, since before they were even known as “urban villages.” She left us with a heavy comment—that the era of urban villages had reached its end. Yang Qian believed that urban villages such as Hubei symbolized the collective memories of Shenzhen people, which is what they are losing as a city. This was part of his motivation to join Hubei 120 and advocate for Hubei’s preservation. He told us about his role in Hubei 120 and how it operated as a leaderless movement. He also made an interesting observation about the shifting image of rural people in China’s popular culture, from farmers to migrant workers, gradually losing a concrete face and identity.
Shi Jie told us about how he became involved in Hubei 120, the growing number of artists creating socially engaged art in the urban villages, and their tensions and strategies in coping with the economic and political realities. As the conversations went on, we noticed that questions about shared memories and belonging often drew answers about loss and segregation.
The Shifting Value of Urban Villages in Shenzhen
When viewed from the perspective of Shenzhen’s development, it seems the city struggles to remember, prone to forgetfulness. Shenzhen issued the Urban Renewal Method for revamping its image as a world-class metropolis in 2009 by calling on real estate developers to bid on original proposals for remodeling urban villages, which over the years have led to their large-scale demolition (Liu et al. 2017, 7). On the one hand, the large-scale project drew from urban villages the “useful” aspects, that which is solid and lasting, while the other aspects were considered redundant and disposable, destined for oblivion. In Hubei, what has been deemed useful are the shrines and ancient landscape, which could be transformed into consumable sites of spectacle, while , appear to be defined as something transitional and thus not worth keeping, despite their vital role in the residents’ livelihoods and historical significance in Shenzhen’s development.
On the other hand, what is considered useful by the city could also be volatile and ephemeral when viewed from a longer, historical perspective. As recently as the 1990s, urban villages—still known as “new villages” at the time—were praised as the essential, useful parts of the city. The transformation from “old villages” to “new villages” and the construction of large numbers of handshake buildings were a self-organized innovative solution that helped address a city-wide housing shortage as well as other issues brought about by the city’s reform. Ironically, although new villages had been recognized as valuable resources and celebrated as a huge success of Shenzhen’s development, their title of “new” was shortly downgraded in the mid-2000s (O’Donnell 2021, 58). The name “urban village” replaced “new village,” and what followed were demolition, renovation, and the social stigmas of filth, disorder, and substandardness. At the end of the day, the new, the solid, and the useful in Shenzhen tend to have transient qualities, sometimes decaying quickly from the city’s collective memory.
Alongside disappearing memories of the villages are unfulfilled dreams of belonging. In recent years, Shenzhen had been advertising its dedication to social inclusion by promoting the slogan, “If you come, you are a Shenzhener” (Shenzhen Government Online 2022). But the demolition and renovation of urban villages and the resulting massive displacement of their residents make this slogan ring increasingly hollow. Urban villages had provided affordable living conditions to most rural migrants to Shenzhen from the 1980s (Hao 2011, 217–18). Due to hukou, a household registration system intended to keep people in place by dividing them into rural and urban categories based on their place of origin, migrants who held rural hukou had for decades faced segregation in the city, including limitations on job opportunities, restrictions in the housing market, and exclusion from many social welfare programs (Cheng 1994, 644–45). Inexpensive and convenient urban villages were essentially shelters for rural migrants, providing access to urban-level resources such as economic opportunities, educational institutions, hospitals, and cultural institutions.
Ironically, in a promotional video in 2020 by China Central Television, the largest state-owned broadcaster in China, the authorities presented the renovation of Nantou Gucheng, an ancient village in Shenzhen, as a successful materialization of the slogan (China Central Television 2020). The city created discourse portraying the construction of a symbolic identity, which supposedly can be achieved by refurbishing old neighborhoods and ancient landscapes. As the refurbishment continues, countless urban villages in central Shenzhen have been transformed into high-end residential areas, glossy consumer destinations, and grandiose landmarks, displacing vast numbers of lower-income communities in the meantime. This identity-building process redefines who is actually treated as Shenzheners, leaving many migrants who have contributed significantly to the city’s economic development out of the picture.
Buildings over People
This renovation method reflects a fixation on buildings over people who live in them. Both the local government and the real estate developers claimed to be protectors of the ancient village in Hubei, notwithstanding their plans to displace entire communities and demolish two-thirds of the ancient village. Even the strategies of Hubei 120 ended up prioritizing preserving the old architecture of Hubei over protecting the communities, despite conflicting voices within the group. It fought with the government and real estate developers over the precise square meter of ancient villages that would be preserved (Yang 2017).
As I went through the footage and interviews of this research trip, I caught a glimpse of how the city might remember itself in the future. It would consist of a solidified past that is over hundreds or thousands of years old, symbolized by renovated ancient villages like Nantou and Hubei, as well as a forever-new present, encapsulated in the skyscrapers that grow taller and taller—yet nothing in between.
References
Cheng, Tiejun, and Mark Selden. “The Origins and Social Consequences of China’s Hukou System.” The China Quarterly 139 (1994): 644–68. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0305741000043083.
China Central Television. “Xianxing: Episode Five [先行 第五集].” Accessed May 10, 2022. https://tv.cctv.com/2020/10/19/VIDEQx2rjSiFM0zzlTT4yehU201019.shtml?spm=C55924871139.PT8hUEEDkoTi.0.0.
Hao, Pu, Richard Sliuzas, and Stan Geertman. “The Development and Redevelopment of Urban Villages in Shenzhen.” Habitat International 35, no. 2 (2011): 214–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2010.09.001.
Liu, Guiwen, Zhiyong Yi, Xiaoling Zhang, Asheem Shrestha, Igor Martek, and Lizhen Wei. “An Evaluation of Urban Renewal Policies of Shenzhen, China.” Sustainability 9, no. 6 (2017): 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9061001.
O’Donnell, Mary Ann. “The End of an Era?: Two Decades of Shenzhen Urban Villages.” Made in China Journal 6, no. 2 (2021): 56–65. https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.287948270260541.
Shenzhen Government Online. “You Are a Shenzhener Once You Come to Shenzhen.” Accessed May 10, 2022. http://www.sz.gov.cn/en_szgov/news/infocus/visa/expat/content/post_7900720.html.
Yang, Qian. “Hubei Observation 3 [湖贝观察 3].” The Paper, August 17, 2017. https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_1762649_1.