That modernity does not necessarily bring secularisation in most parts of the world is knowledge rarely disputed in our times. People working in the field of development are increasingly acknowledging the continuing influence of patriarchal2 religious norms on individual and collective life and looking for ways to promote female empowerment within the local reality.3 At the same time, there is growing evidence that gender-specific programmes in the past have produced negative side effects, perhaps because they failed to understand the interdependent livelihoods of men and women in traditional societies. This has led to some efforts to make men and boys central actors of female empowerment.4 Ordinary women in more traditional societies still grapple with culture-specific challenges that are rarely addressed in global initiatives. These include fundamentalist wars against their piety, frictions between modernisation and cultural identity, and intergenerational communication problems that interfere with young women’s choices.5
These were some of the challenges local people repeatedly conveyed to me through their accounts during a year of research in sub-Saharan Africa. The project described here was designed in response to these findings, and proposes to address asymmetries in the lifestyles and livelihoods of men and women working through the patriarchal institutions that inevitably make up the building blocks of most traditional societies. Pragmatic development must be relevant to the realities of local people, and must work within those realities to create an environment for change from within that is led by the people themselves out of their free choice.
Background
The idea that development programmes need to be cautious not to promote existing inequalities between men and women is the product of Western feminist movements. Gender sensitivity has been a mainstream part of development since at least the 1995 International Conference on Women held in Beijing.6 In 2013, in an attempt to understand the need to integrate gender-sensitivity in African agricultural development programmes, I embarked on a year-long fieldwork project in Ghana, Ethiopia, Rwanda, and Tanzania.7 My methodology was to listen to what men and women had to say about their livelihoods, to observe how men and women lived together, and to become exposed to Western gender and development approaches so as to investigate their impact.
The findings overall revealed a gap between people’s nuanced lifestyles (and the even more nuanced relationships between men and women) and the theoretical assumptions underpinning most gender and development programmes. The mainstream theoretical framework seemed to be premised on a consistent set of assumptions about gender relations in other countries and the implicit idea that most cultural influences are pernicious to women. In addition, the fact that gender analysis was done from the standpoint of leading Western societies meant that the impact of faith on material life was rarely researched or accounted for. In the societies where I lived, however, it was evident that cultural and faith-based ideas and beliefs shaped gender identities and relations, also influencing women’s possibilities as food producers. It was rarely recognised in the programmes I saw that improving women’s livelihoods would require understanding and engaging with these deeply embedded ideas and socialisation norms first. I therefore developed an alternative strategy that would include traditional institutions both in the analysis of gender realities and in sensitisation processes. Getting local religious and patriarchal figures involved in this process was another priority.
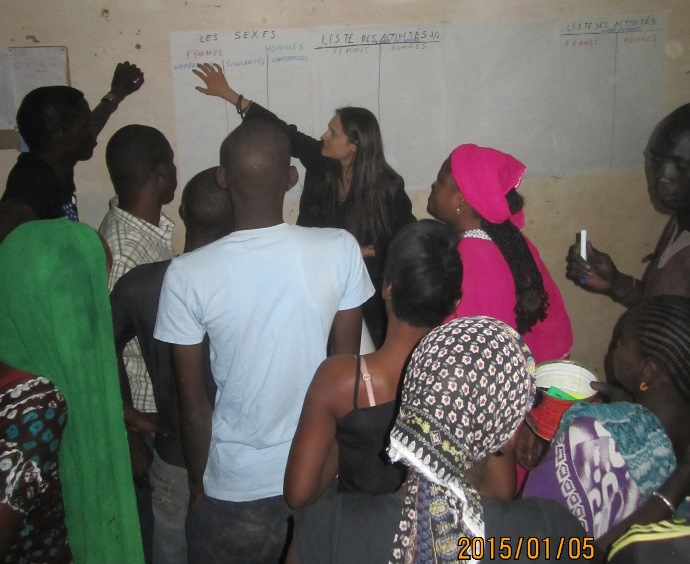
My proposal was to achieve this by combining ethnographic methods of research with participatory methodologies for community discussion. The process of group sensitization would be guided by ERDA methodology, a tool developed by research partners at the University of Tennessee to promote collective problem solving in communities.8 Through such a process of collective dialogue participants were expected to become more aware of the positives and negatives in their community. The gender-sensitive aspect of the approach would in turn provide a platform for thinking about asymmetries in the livelihoods and social roles of men and women, and trace their origin possibly in religious and cultural conventions. At the same time, ERDA would guide the process of sensitization and reduce my role to that of interlocutor. I employed this approach for the first time in the community of Guédé Chantier in Senegal, in response to an invitation by the mayor, Dr. Ousmane Aly Pame, to support the community’s development in ways that would be inclusive and culture-sensitive.9
Socio-economic Conditions through the Gender Lens in Guédé Chantier
Guédé Chantier was established in 1933 by the French colonial administration as an irrigated agriculture project, resettling some 50 families to the area to grow rice. The original local inhabitants were Fulani, although today Guédé is ethnically diverse. The population is homogenously Muslim, with the majority belonging to the Sufi branch of Islam, and specifically the Tidjanniya brotherhood.10 Guédé has a population of approximately 7,000, with a large population of young women.
Men are expected to provide for their families. They usually work in pastoralist, agricultural, fishing, artisanal, and entrepreneurial activities in the village and nearby areas. Women are responsible for looking after children and running the house. Many women work small parcels of land to produce vegetables, which they sell to buy cooking materials. Almost all women are involved in the transformation of raw foodstuffs for sale, including preparing salted peanuts and turning rice into flour.
Currently the community faces a number of problems, including soil depletion, water pollution due to use of synthetic fertilizers, shortage of pastoral land, drought, unstable income due to seasonal problems, and migration. Women have limited control of land, limited access to agricultural inputs, and find it difficult to secure credit. Livelihoods for both men and women are becoming more difficult as the price of living increases. This is felt particularly by women, who must manage daily household needs on very meagre funds.
Project Activities
A. Context Analysis
The project was planned as three rounds of activities to unfold over the period of one year. In the first round, I completed questionnaires with men and women in their homes that asked them about their livelihoods and gender-specific challenges. I also spoke to key informants, representatives from local youth organisations, and ordinary men and women. Two focus group discussions—one with men and another with women—were held to unpack profounder religious and cultural beliefs and norms underpinning girls’ and boys’ socialisation. This information was used to prepare the participatory workshop.
B. Participatory Workshop
The workshop had a timeline of two days; it attracted 14 participants on the first day, and 21 on the second (38% female). The group was diverse in terms of age, education levels, marital status, and other socio-economic characteristics. 11 The workshop followed the ERDA methodology, starting with an evaluation of current realities, followed by exercises to bring out problems caused by the intersection of traditional values and norms and modern influences, to assess possible needs and opportunities, and ultimately to produce a platform for action toward sustainable community growth.
In the second part of the workshop, a conversation about moral values led participants to examine their ideas and perceptions about people from different backgrounds, and the issue of equality and difference. This led gradually to the topic of the relations between men and women in Pulaar society. Young men and women, both married and single, worked together to list differences and similarities between men’s and women’s livelihoods. Participants also discussed the impact of family, schooling, and religious education on their perceptions about women and men and their respective roles in society. A conversation about spousal and inter-generational communication followed. Although disagreement occasionally halted dialogue early on, by the end of the workshop participants were fully engaged and more aware of their shared identities than differences. Participants also expressed excitement at the ERDA methodology, which they felt could be replicated to promote other communal development initiatives.12
C. Meeting with Patriarchal Leaders
In the second round of activities a meeting was held with religious leaders: Muslim clerics and local elders (a total of nine participants). I planned this discussion to summarise the participatory workshop and its findings to the local ‘patriarchs,’ and to discuss issues of equality in Islam as they had been articulated during the workshop, the focus groups and the personal interviews. The aim was to hear how local leaders thought about the intersection of faith-based, culturally embedded norms about men and women and the needs of younger generations in a constantly globalising world. I also wanted to see how they would visualise development in their community, and their role and responsibility in it.
Progress and Future Directions
The ethnographic activities showed that men and women have different roles, responsibilities, and expectations in this society. The asymmetries in livelihoods most likely reflect religious norms compounded by cultural practices. Patriarchal arrangements of social life, such as in the ways land is allocated, did seem to make equality more difficult to sustain. But the real impediment was found in mentalities that viewed women as less capable than men and belonging exclusively in the home. The participatory workshop showed that most people are interested in change and condone equality, but in ways that do not depart from patriarchal structures that they perceive as foundational to either faith or culture. Any intervention that aims to address women's problems would need to take into account this subtle relationship between growing ideas of equality and a strong sense of identity, especially in cases where the latter combines with an androcentric worldview.
It also emerged from the activities that there is much untapped potential for personal and economic growth in women’s agricultural and revenue-generating activities at home. From the conversation with religious leaders it became evident that they would not oppose economic activities led by women, although there was a general preference that women should not work. Because women spend most of their time within the house, growing food in gardens was identified as a possible pathway for providing women with a stable and independent source of income, and also improving their children’s nutritional habits in the long run (which currently lack diversity).
Subsequently, in a third trip to the village, a workshop was held with women on the themes of nutrition and agriculture. The workshop again employed the ERDA methodology of collective dialogue. In the discussions, women recognised linkages between cultural influences and tradition and current nutritional practices and deficiencies, and raised the need for change. Some participants proposed forming an association for women that would pilot a collective project to grow more nutritionally rich foods at the established local genetic centre. In line with this project’s premises that change must be free-willed and start from within, it was left to the local population to decide how they will leverage on the ERDA activities and what changes they will proceed to make.13
Objectives, Aims, and Expectations
This project’s objective has been two-fold: first, to see more community members sensitised about differences and asymmetries in the lifestyles and livelihoods of men and women, and second to create an environment for men and women to come together, discuss their problems and needs, and become aware of new collective and individual pathways for action. The underlying aim was to pilot a new approach to development practice that is based on local gender knowledges, and does not attempt to impose change based on a priori conceptualisations of what ideal gender relations should be. The activities in the village also provided the context for my masters research titled “Gender through the Lens of Religion: An Ethnographic Study from Senegal” (University of Sussex, Institute of Development Studies), which should add to the field’s understanding of the intersection of faith-based worldviews and Western ideas of gender equality, as well as the implications of this intersection for sustainable development in African societies and elsewhere.14
“Power lies with the individual who has the freedom of choice. This choice, however, requires will, maturity and knowledge.” Young woman in Guédé Chantier
1I would like to thank sincerely the Tokyo Foundation in Japan for believing in the proposal I submitted, and for granting me the means to begin to realise it. I also want to thank Dr. Harwood Schaffer at the University of Tennessee for sharing his work with me and introducing me to the community of Guédé Chantier, and its first Mayor Dr. Ousmane Pame, for willingly accepting my proposal and facilitating my fieldwork and activities there. I also wholeheartedly thank the population of Guédé Chantier for accepting me and for showing patience and willingness to engage with this endeavour.
2‘Patriarchy’ etymologically results from the combination of two words, pater>patria and arkhein, which mean respectively ‘father>family/clan’ and ‘to begin/to rule/to command’ (Online Etymology Dictionary). Patriarchy here then is not defined as androcentrism, but as an organisational structure in which the male plays a central role. Whether a male-led institution becomes unequal will depend on how that subject uses the authority given to him.
3See for example E. Tomalin (ed.), 2015, The Routledge Handbook or Religions and Global Development. Routledge.
4See for example E. Esplen and A. Brody, 2007, Putting Gender Back in the Picture: Rethinking Women's Economic Empowerment, http://www.bridge.ids.ac.uk/sites/bridge.ids.ac.uk/files/reports/BB19_Economic_Empowerment.pdf
5It is little surprise that many scholars in developing countries continue to call for alternative epistemological approaches to gender theorisation. See for example O. Oyěwùmí, (ed.), 2011, Gender Epistemologies in Arica: Gendering Traditions, Spaces, Social Institutions, and Identities, Palgrave McMillan. The same position is echoed in anthropological arguments that have long called for practice designed on the basis of local knowledge. See for example L. T. Smith, 1999, Decolonizing Methodologies Research and Indigenous People, London: Zed Books Ltd.
6See for example C. Moser, 1993, Gender Planning and Development: Theory, Practice and Training, Routledge: London and New York.
7I was awarded the Thomas J. Watson fellowship by the eponymous foundation in New York after being nominated by Bates College in 2012. The project was of my own conceptualisation and design, and was implemented during the period of one year.
8This tool was developed by research partners at the University of Tennessee. It is known by the acronym ERDA (Evaluate, Research, Develop and Assess), and according to my partner, Dr. Harwood Schaffer, was adapted from a well-known tool in Business Studies called Cycle of Innovation. It was designed to set in motion an ongoing cycle of community insight-sharing and re-assessment, securing community ownership of decision-making, to encourage cooperative problem-solving. It was developed on the idea that when practitioners depart, the community must be able to continue to resolve its problems independently.
9Dr. Pame as introduced to me through my research partner at the University of Tennessee, who was at the time working closely with Dr. Pame to address agriculture-related issues in the community. Since Guédé Chantier was upgraded to the status of a commune (2008-2009), Dr. Pame has been committed to mobilising its local population toward more sustainable growth pathways. The community was reportedly the first to be registered as an eco-village.
10Sufism is the mystical version of Islam, and is defined by the followers’ search for inner spirituality and approximation of God. The Tidjanis share three foundational principles, which are: 1. Praying to be forgiven for your sins (‘Astafiroullah’), 2. Recognising no one as divine but God (‘La Illa Ha Illalah’), 3. Praying to the Prophet Mohammad (‘Salatou Allale Nabby’). (Principal Imam Abdoulaye Ly, personal interview, 1 April 2015, consent granted).
11Participation at this point was self-selected, however an attempt was made to communicate directly with women and men in the community so as to ensure that everyone was informed before the day of the workshop.
12Participants proposed various suggestions, but due to the fact that we ran out of time, no action plan was created. The different pathways were discussed in follow-up conversations.
13My conviction is that development must respect free choice. This echoes the work of Amartya Sen (Nobel Prize in Economics 1998). My approach takes Sen’s theory seriously and recognises that people value different things and that development must be formulated based on such values. See A. Sen, 1999, Development as Freedom, Oxford University Press.
14This has become my MA dissertation at the Institute of Development Studies (IDS), University of Sussex, under the title “Gender through the Lens of Religion: An Ethnographic Study from a Muslim Community in Senegal”.